Mahadevpura, Bangluru-560037
Mahadevpura, Bangluru-560037 [email protected]
[email protected] +91 9026187944
+91 9026187944
If you've ever wondered how the internet works behind the scenes—from clicking a link to receiving data from a server—the OSI Model is the framework that breaks this process into seven understandable steps. This model helps students, IT professionals, and developers understand how data moves through a network and where different technologies operate.
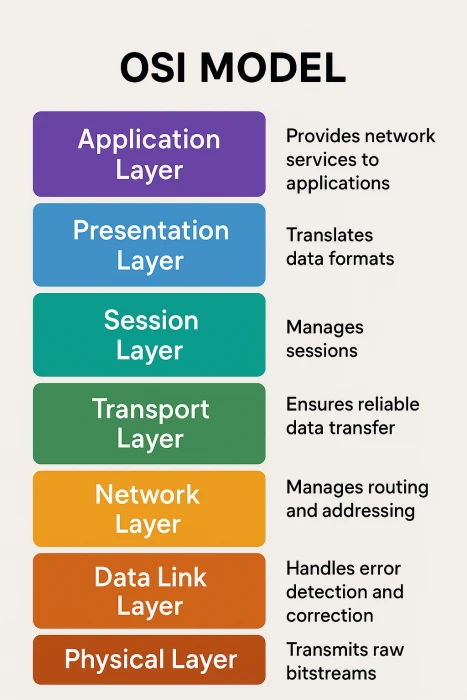
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model is a theoretical framework that standardizes network communication into seven layers. Each layer has a specific role and communicates with the layers directly above and below it.
Think of it like sending a letter: you write the message, put it in an envelope, address it, and finally mail it. Each step corresponds to a layer.
Function: Interface between user applications and the network.
Examples: Web browsers, email clients, FTP software.
Common Protocols: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, DNS
Ports:
HTTP – Port 80
HTTPS – Port 443
FTP – Ports 20 & 21
SMTP – Port 25
DNS – Port 53
?? Example: When you type
www.google.comin your browser, HTTP (or HTTPS) works at the Application Layer to start the process.
Function: Translates data formats, handles encryption/decryption and compression.
Examples: JPEG, MP4, SSL, TLS
Real-Life Use: Converting text characters to a readable format or encrypting data for secure websites.
? Example: TLS encrypts your data on an HTTPS website to keep your information safe.
Function: Manages sessions or connections between devices. It opens, maintains, and terminates communication.
Examples: NetBIOS, RPC, PPTP
? Example: When you're in a Zoom meeting, the Session Layer ensures that your communication with the server is ongoing and stable.
Function: Ensures reliable data transmission, handles flow control and error checking.
Protocols: TCP (reliable), UDP (fast but unreliable)
Ports:
TCP – Port 443 (HTTPS), Port 80 (HTTP)
UDP – Port 53 (DNS), Port 69 (TFTP)
? Example: Downloading a file uses TCP to ensure every piece arrives correctly. Online gaming often uses UDP for speed.
Function: Determines the best path for data and handles IP addressing.
Protocols: IP (IPv4, IPv6), ICMP (ping), OSPF, BGP
Devices: Routers
? Example: When sending data across different networks, IP helps route it to the correct destination.
Function: Handles node-to-node data transfer and error detection. Uses MAC (Media Access Control) addresses.
Protocols: Ethernet, PPP, ARP
Devices: Switches, Bridges
? Example: When your device connects to Wi-Fi, it uses a MAC address to communicate with the access point.
Function: Transfers raw bits over a physical medium.
Examples: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, Wi-Fi signals
Devices: Hubs, repeaters, cables, network interface cards (NICs)
? Example: The actual cable that connects your PC to the router.
| Layer | Name | Example Protocols | Devices or Ports |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | HTTP, FTP, SMTP | Port 80, 443 |
| 6 | Presentation | SSL, TLS, JPEG | - |
| 5 | Session | NetBIOS, RPC | - |
| 4 | Transport | TCP, UDP | Port 20–443 |
| 3 | Network | IP, ICMP, OSPF | Routers |
| 2 | Data Link | Ethernet, ARP | Switches, MAC |
| 1 | Physical | Wi-Fi, Cables | NICs, Cables |
From Layer 7 to 1 (Top to Bottom):
"All People Seem To Need Data Processing"
From Layer 1 to 7 (Bottom to Top):
"Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away"
Understanding the OSI Model helps you:
Troubleshoot network issues by isolating problems to specific layers.
Understand how firewalls, ports, and IP addresses function.
Communicate effectively with networking professionals.
The OSI Model isn't just for theory exams—it's foundational knowledge that underpins all modern networking. Whether you're working in cybersecurity, web development, or just setting up your home network, knowing what happens at each layer can give you a clearer understanding of the internet's invisible machinery.